Many people feel discouraged when thinking of dealing with Linux, but I’m here to tell you it’s not so complicated. Today, I will share with you the top 50 Linux commands from Basic To Advance. I made it to motivate and push you to start working online. I am going to show you 50 Linux commands that will make your Linux work-life easier.
learn the 50 most popular Linux commands all these commands work on Linux, Mac OS, and any other place you have a Unix environment.
My name is Deep Vempati and today we are going to learn a ton about the command line and different Linux commands I’m a DevOps Engineer, well honestly more of a Techie who happens to write code I teach in-person about DevOps and other tech stuff through this blog.
Contents
- 1 Linux Commands Basics Cheat Sheet
- 1.1 1. What is WHOAMI command in Linux
- 1.2 2. What does MAN command use in Linux
- 1.3 3. Clear
- 1.4 4. Options
- 1.5 5. PWD
- 1.6 6. Ls
- 1.7 7. Cd
- 1.8 8. Mkdir
- 1.9 9. Touch
- 1.10 10. Rmdir
- 1.11 11. Rm
- 1.12 12. Open
- 1.13 13. Mv
- 1.14 14. Cp
- 1.15 15. Head
- 1.16 16. Tail
- 1.17 17. Date
- 1.18 18. redirecting standard output
- 1.19 19. cat
- 1.20 20. less
- 1.21 21. echo
- 1.22 22. WC
- 1.23 23. What is a Pipe in Linux?
- 1.24 24. sorts
- 1.25 25. Uniq
- 1.26 26. Expansions
- 1.27 27. Diff
- 1.28 28. Find
- 1.29 29. Grep
- 1.30 30. Du
- 1.31 31. Df
- 1.32 32. History
- 1.33 33. Ps
- 1.34 34. Top
- 1.35 35. Kill
- 1.36 36. Killall
- 1.37 37. Jobs, BG, and FG
- 1.38 38. Gzip
- 1.39 39. What is the use of gunzip command in Linux?
- 1.40 40. Tar
- 1.41 41. Nano
- 1.42 42. Alias
- 1.43 43. Xargs
- 1.44 44. Ln
- 1.45 45. Who
- 1.46 46. Su
- 1.47 47. Sudo
- 1.48 48. Passwd
- 1.49 49. Chown
- 1.50 50. chmod
- 2 Conclusion
Linux Commands Basics Cheat Sheet
So we are going to cover 45 actually I think it’s a little more than 45-50 commands that are useful.
If you’re a beginner you can start at the beginning and we’ll go through the basics navigation working with the basic commands and options and making folders and files and so on but then after about this point things really open up and you can jump around to whatever commands you’d like and of course if you’re someone who already has some terminal experience some of these commands are familiar to you just hop around take a look at the TABLE OF CONTENT and just click on whatever command you’re not really comfortable with.
1. What is WHOAMI command in Linux
Whoami is going to print the username of the currently logged-in user so maybe not be something you need to do all the time. you probably know who you’re logged in to as though there are uses for this, especially in scripting if you write scripts later on you might want to know which you are logged in to.
2. What does MAN command use in Linux
The next command we’ll look at is called man the man command m-a-n is short for manual and that’s exactly what it is. It is a command that doesn’t do anything to our system it’s purely informative it tells us information or manual pages for other commands. and this is the one of the useful command in this linux commands basic to advance.
3. Clear
Clear is a Linux command that is used to clean the terminal screen from the previous command and gives you a blank terminal screen However you can always see your previous commands by clicking on 🔼.
4. Options
Options are not actually are the commands, these are the extensions for the commands in Linux to get additional advantages. Options are used on the command line (the all-text display mode) following the name of the command and before any arguments.
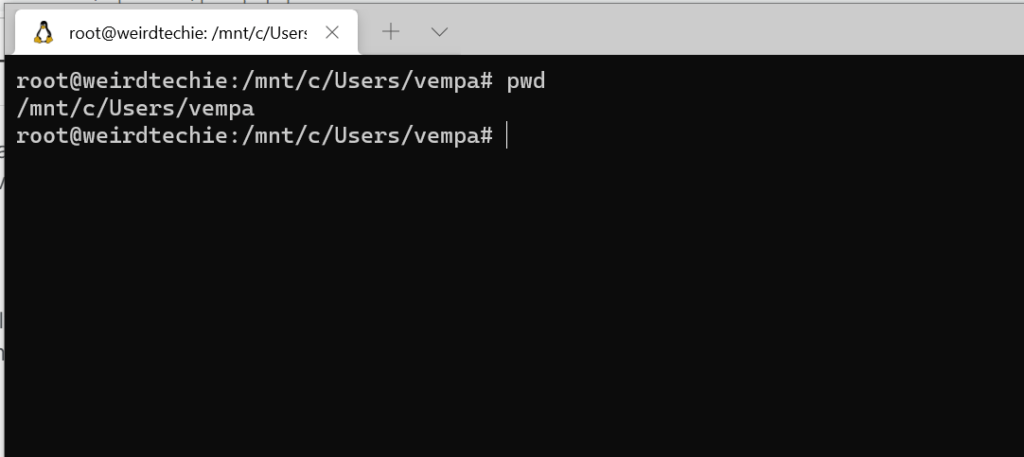
5. PWD
The full form of PWD is Present Working Directory and this command helps you to check/know on which path you are in as shown in the below picture
6. Ls
LS stands for lists and is used to list files. It shows all files in the current directory except for hidden files.
7. Cd
The cd command means Change directory, It is used to change the current working directory in various operating systems. The cd command, also known as chdir
EX: if you are in the root directory and want to go to the home directory which is inside the root directory then you can use this command below
Root://$ CD home Root>home/$
8. Mkdir
The mkdir (make directory) command is used to make a new directory. For suppose you need to create a directory/folder in your Linux system then you can use Mkdir to create a directory as shown in the image below

9. Touch
The “Touch” command is a standard command used in UNIX and Linux operating systems which is used to create, change and modify timestamps of a file.
10. Rmdir
The rmdir command is used to remove/delete the directory, specified by the Directory parameter, from the Linux or Unix system. But the directory must be empty before you can remove it.
11. Rm
Rm commands stands for “Remove”. The rm command is used to delete files.
12. Open
The open command lets open a file using this syntax: open <filename>.
13. Mv
Mv commands stands for “Move”. The mv command is used to Move files from one directory to another directory.
14. Cp
Cp commands stands for “Copy”. The cp command is used to Copy files from one directory to another directory.
15. Head
The head command helps you to print the top N number of data of the input given by the user. By default, it prints the first 10 lines of the specified files. If more than one file name is provided then data from each file is preceded by its file name.
16. Tail
Tail is the Unix/Linux command utility, that is used to display the tail end of a text file or piped data. The tail command helps to display the last 10 lines by default of one or more files or piped data. It can also be used to monitor the file changes in real-time.
17. Date
The date command is used to display the system’s date and time. The date command can be used to set the date and time of the system. But you must be the super-user (root) to change the date and time on any Linux /Unix system.
18. redirecting standard output
Redirection is one of the features of Linux and Unix systems such that when executing a command, and user can change the standard input/output devices.
19. cat
Cat is a very frequently used command in Linux. It reads data from the file and gives its content as output to view.
20. less
Less is a Linux command that can be used to read the contents of a text file one page at a time. It is an easy way to read files than CAT command if a file is large. LESS command doesn’t access the complete file but accesses it page by page.
21. echo
echo command in Linux is used to display lines of string or text that are passed as an argument. echo is the command that is used in Linux /Unix system and works as same as the PRINT command in programming languages. This is a built-in command that is mostly used
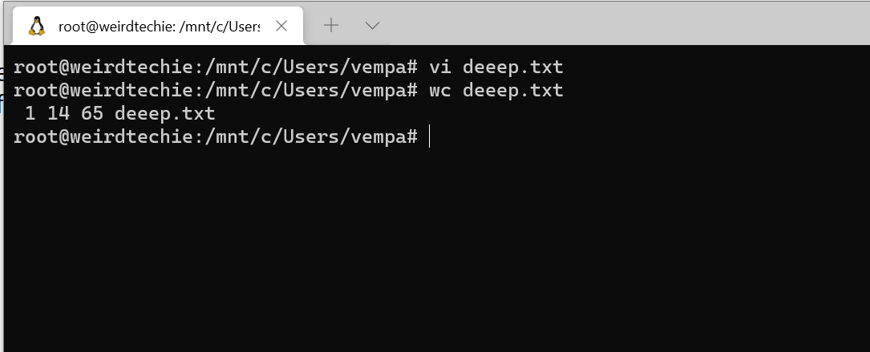
22. WC
The ‘wc’ stands for word count. It has a quite simple syntax. It lets you count the number of lines, words, bytes, and characters in one or multiple text files. The first number would be how many lines, the second number should be how many words are there in the given text file, and at last will be the size of the file in bytes
As per the below Image the Deeep.txt file has 1 line, 14 words 65bytes
23. What is a Pipe in Linux?
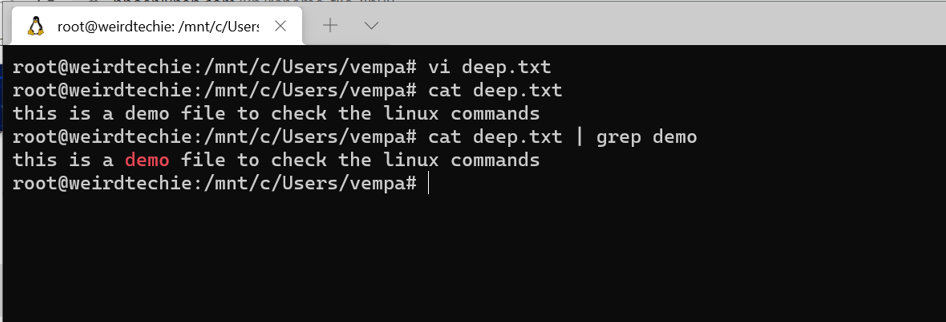
The Pipe is a command that allows you to use two or more commands such that the output of one command serves as input to the next. In other words, the output of each process is direct as input to the next one like a pipeline.
The pipe command is used with | and you can see the example in the below image
24. sorts
The sort command is used to display the content of the file in alphabetical order as shown in the below image. The first output is the original output and the second output is the one in alphabetical order.
25. Uniq
The uniq command in Linux is a command-line utility that reports or filters out the repeated lines in a file.
In other words, the uniq command removes the duplicate lines in the file and shows the unique sentences.
Also read: How To Install Jenkins In Ec2 Instance
26. Expansions
Expansions is not a command, When a command is entered in the CL (command line), it expands into its output which is displayed. This is called expansion. The command you’re typing will be printed with the help of echo command on the terminal.
Example: echo “*” output *
27. Diff
diff command stands for the difference. Diff is used to display the differences between the files by comparing the multiple files line by line.
28. Find
In Unix and Linux operating systems, find is a command-line that helps to locate files based on some user-specified criteria and either print the pathname of each matched object.
29. Grep
Grep is a crucial Unix and Linux command. It is used to search strings and text in a given file. In simple words, the grep command searches the given file for lines containing a match to the given words or strings.
30. Du
The du command stands for Disk Usage. It allows you to check the disk usage information quickly. It is best applied to specific options like -m to show the size of the directory in MD, -g for GB, and so on.
31. Df
The full form of ‘df’ command is the “disk filesystem“, it is used to get a piece of full information on used disk space usage of the file system on the Linux system and available disk space too.
32. History
The history command in Unix/Linux allows you to view the history of the commands that you run in the terminal.
33. Ps
The ps command stands for Process Status. It is used to get information or display related to the processes running in a Linux system.
34. Top
The top command stands for Table Of Processes, It shows a real-time view of running processes in a Linux system and displays kernel-managed tasks. The command also provides system information like CPU and memory usage.
35. Kill
The kill command generally sends a signal to a running process to stop processes. If you want to stop a process, specify the process ID (PID) in the ProcessID variable. KILL uses the SIGTERM signal as default.
36. Killall
The killall command in a Linux command is used for killing any running process on the system based on a given name you provide. killall command will terminate/kill the processes forcibly when a specified name matches the given name to currently running processes.
37. Jobs, BG, and FG
-> FG: The full form of FG is foreground, You can use the fg command to bring a background job to the foreground.
-> BG: The bg command full form of background. BG restarts a suspended job and runs it in the background. If there is no job number is specified, then bg or fg command acts upon the currently running job.
38. Gzip
Gzip is also known as GNU zip. Gzip is a free and open-source algorithm for file compression. The software is overseen by the GNU project. In this context, compression is the deliberate reduction in the size of data to save storage space or increase the data transfer rate.
39. What is the use of gunzip command in Linux?
Gunzip command is used to compress or Extract a file or a list of files in Linux. It works on all the files having extensions as .gz, .z, _z, -gz, -z.
40. Tar
The tar command is the most widely used archiving utility in Linux and Unix systems. Can be accessible directly in the terminal, the tar command helps create, extract, and list archive contents.
41. Nano
nano is a terminal-based text editor. but not as powerful as Emacs or Vim, but it’s easy to learn and use. Nano is ideally used for making small changes to existing configuration files or used to write small plain text in files.
42. Alias
An alias command is a Linux utility and it is a shortcut command to a longer command. You can type the alias name to run the longer command with less typing. Without arguments, the alias prints a list of defined aliases.
43. Xargs
xargs is one of the essential commands that help to read streams of data from standard input, then generates and executes command lines.
44. Ln
“ln” is a Linux command that is used for linking files and directories to each other. ln command allows any number of new names to be created, all pointing to the same file or directory.
45. Who
The Linux “who” command lets users display their current logged-in to your UNIX or Linux operating system. The who cmd is used to get information about currently logged-in users onto the system.
46. Su
The SU is a Unix/Linux command, which stands for substitute user, It is used by a computer user to execute commands with the privileges of another user account mostly to get the Sudo user privileges.
47. Sudo
sudo is a program for Unix-Linux computer operating systems that enables users to run programs with the security privileges of the root(administrator) user, by default the superuser and can be used to run the program with other user security privileges.
48. Passwd
Passwd is a command on Unix and Linux, It is used to change a user’s password
49. Chown
The Chown command is used on Unix and Linux -like operating systems to change/remove/provide the owner of file system files, and directories.
50. chmod
chmod is the command that lets users change the access permissions of file system objects, (files and directories) sometimes known as modes.
Also Read: How To Send Bulk Messages On Whatsapp Using Python Code
Conclusion
These 50 Linux commands from basic to advance Linux and most commonly used in Linux and you can take the command to next level when you use options with these commands, use the MAN command to know more details of any command.
